|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Wi-Fi Signal Weak in One Room? 9 Easy Fixes Without Buying a New Router (2025)

Table of Contents
ToggleTired of that frustrating moment when your video call freezes, your movie buffers endlessly, or your download crawls to a halt—but only in certain rooms of your home? You’re not alone. A Wi-Fi signal weak in one room is one of the most common connectivity issues homeowners and remote workers face today. The good news? You don’t need to invest in expensive new equipment to solve this problem.
In this troubleshooting guide, we’ll explore why Wi-Fi signals drop in specific areas and provide nine practical, budget-friendly fixes you can implement today. From strategic router placement to simple household adjustments, these solutions can dramatically improve your connection without requiring a new router purchase.
Why Is Your Wi-Fi Signal Weak in One Room?
Before diving into solutions, it helps to understand why your Wi-Fi signal weakens in specific areas. Wi-Fi travels as radio waves that can be blocked, absorbed, or scattered by various obstacles:
- Distance from router: Signal strength naturally decreases the further you move from the source.
- Physical barriers: Thick walls (especially concrete, brick, or stone), floors, and metal objects can significantly block signals.
- Electronic interference: Microwaves, baby monitors, and Bluetooth devices operate on similar frequencies and can cause interference.
- Reflective surfaces: Mirrors and metal objects can bounce signals in unpredictable directions.
- Overcrowded networks: Too many devices connected simultaneously can strain your network.
READ ALSO – Phone Storage Full? 11 Best Ways to Free Up Space Instantly
1. Reposition Your Router Strategically
The simplest and most cost-effective fix is often just moving your router to a better location. Your router’s placement significantly impacts signal distribution throughout your home.
How to do it:
- Place your router in a central location rather than at one end of your home
- Elevate the router 4-6 feet off the ground (on a shelf or desk)
- Keep it away from metal objects, appliances, and thick walls
- Ensure it’s not hidden inside cabinets or behind furniture
- Position antennas vertically for better horizontal coverage (if your router has adjustable antennas)
This simple adjustment can dramatically improve coverage in problem areas without costing a penny.
2. Update Your Router’s Firmware
Outdated firmware can cause performance issues that affect signal strength and stability. Manufacturers regularly release updates that improve connectivity, security, and overall performance.
How to update your router:
- Find your router’s IP address (typically printed on the device or in its manual)
- Enter this address in your web browser
- Log in with your admin credentials (also usually on the device)
- Look for “Firmware Update,” “Administration,” or “System” sections
- Follow the prompts to check for and install updates
Many modern routers also offer automatic updates through their companion apps, making this process even simpler.
3. Switch to the 5GHz Band
Most modern routers are dual-band, offering both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies. Each has distinct advantages:
2.4GHz Benefits
- Better range and wall penetration
- Compatible with older devices
- Good for basic browsing and email
5GHz Benefits
- Faster speeds (up to 3x faster)
- Less crowded frequency
- Less interference from household devices
- Better for streaming and gaming
If your problem room is relatively close to the router but experiencing interference, switching to 5GHz might solve your issues. For rooms further away, 2.4GHz might work better despite its lower speed.
How to switch bands:
Most dual-band routers broadcast separate network names (SSIDs) for each band, typically with “5G” or “5GHz” added to the network name. Simply connect to the appropriate network on your device.
READ ALSO – How to Protect Your Kids Online – Best Parental Control Apps
4. Adjust Your Router’s Antennas
If your router has external antennas, their positioning can significantly impact signal direction and strength.
Antenna positioning tips:
- Vertical antennas spread signal horizontally (best for single-floor coverage)
- Horizontal antennas spread signal vertically (better for multi-floor homes)
- For multiple antennas, position them perpendicular to each other for optimal coverage
- Point one antenna directly toward the problem room for focused signal boost
Experiment with different positions to find what works best for your specific layout.
5. Eliminate Interference Sources
Many household devices operate on the same frequency as your Wi-Fi, causing interference that weakens your signal in specific areas.
Common interference culprits:
- Microwave ovens
- Cordless phones
- Baby monitors
- Bluetooth devices
- Wireless speakers
- Neighboring Wi-Fi networks
How to reduce interference:
Identify which devices might be causing problems in your weak signal room. Move your router away from these devices or vice versa. For devices that can’t be moved, try not to use them when you need reliable Wi-Fi in the problem area.
You can also use a Wi-Fi analyzer app to identify which channel your network is using and switch to a less congested one through your router’s admin panel.
6. Use a DIY Signal Reflector
Before investing in new equipment, try this surprisingly effective DIY solution that costs almost nothing.
How to make a Wi-Fi reflector:
- Cut a piece of cardboard roughly 8×11 inches
- Cover one side completely with aluminum foil
- Curve it slightly into a parabolic shape
- Place it behind your router with the foil facing toward the problem room
This simple reflector works by focusing radio waves in a specific direction, potentially boosting signal strength by 2-4 dBm in the targeted area.
7. Change Your Router’s Channel
Wi-Fi routers operate on specific channels within their frequency bands. In crowded areas like apartments, channel congestion can significantly impact performance.
How to change your router’s channel:
- Download a Wi-Fi analyzer app (like WiFi Analyzer for Android or Airport Utility for iOS)
- Scan nearby networks to identify the least congested channels
- Access your router’s admin panel
- Find the wireless or channel settings
- Select a less crowded channel (1, 6, or 11 are typically best for 2.4GHz)
For 2.4GHz networks, channels 1, 6, and 11 are recommended as they don’t overlap with each other. For 5GHz, any channel with low usage in your area will work well.
READ ALSO – How to Stop Spam Text Messages on Android & iPhone
8. Enable Quality of Service (QoS) Settings
Quality of Service (QoS) settings allow you to prioritize certain types of internet traffic, ensuring critical applications get bandwidth priority.
Benefits of enabling QoS:
- Prioritize video calls when working from home
- Ensure smooth streaming in entertainment areas
- Reduce gaming lag even when others are using the network
- Prevent large downloads from affecting important activities
How to enable QoS:
Access your router’s admin panel and look for “QoS,” “Traffic Management,” or similar options. Most modern routers allow you to prioritize specific devices or applications. Some even have presets for common activities like gaming or video conferencing.
9. Use Powerline Adapters for Problematic Rooms
If all else fails, powerline adapters offer an elegant solution without requiring new Wi-Fi equipment. These devices use your home’s electrical wiring to transmit internet signals between rooms.
How powerline adapters work:
- Plug one adapter into an outlet near your router and connect it via Ethernet
- Plug the second adapter into an outlet in the problem room
- Connect your device to the second adapter via Ethernet or Wi-Fi (if it has built-in Wi-Fi)
This solution effectively bypasses Wi-Fi dead zones by using your existing electrical wiring as a network cable. Modern powerline adapters can achieve speeds up to 2000 Mbps, more than enough for streaming, gaming, and video calls.
How to Check If Your Fixes Are Working
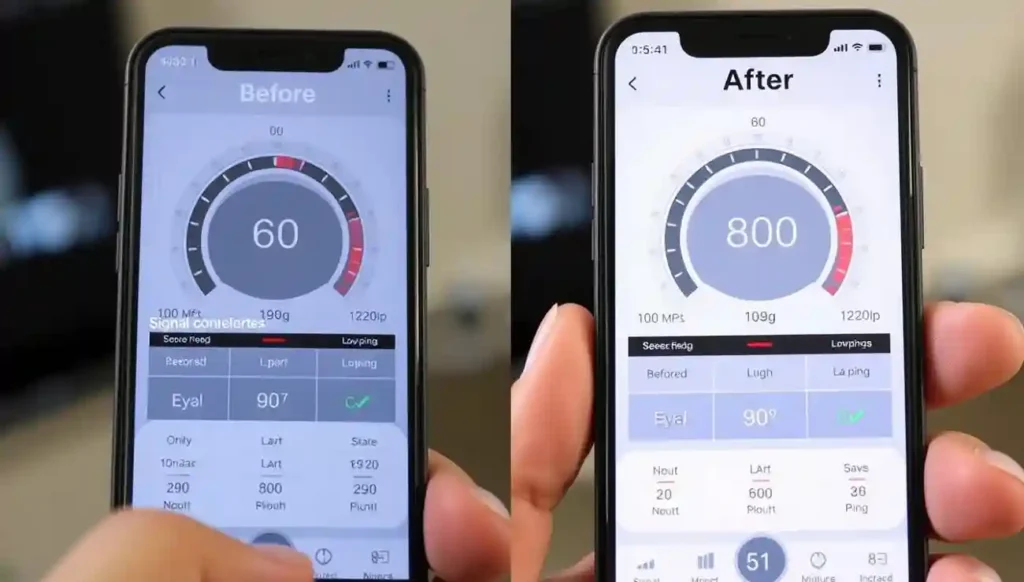
After implementing these fixes, it’s important to measure your improvements objectively:
- Run speed tests in the problem room before and after making changes (using services like Speedtest.net or Fast.com)
- Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app to measure actual signal strength in dBm (closer to 0 is stronger)
- Test real-world usage with video streaming, conference calls, or other bandwidth-intensive activities
Remember that combining multiple fixes often yields the best results. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different combinations to find what works best for your specific situation.
READ ALSO – How to Stop Apps from Tracking You – Android & iOS Tips
Conclusion: Enjoy Better Wi-Fi Without Buying New Equipment
A Wi-Fi signal weak in one room doesn’t necessarily mean you need to invest in expensive new equipment. As we’ve seen, strategic adjustments to your existing setup can dramatically improve coverage throughout your home.
Start with the simplest fixes—repositioning your router, updating firmware, and eliminating interference—before moving on to more involved solutions. Often, a combination of these approaches will solve even the most stubborn connectivity issues.
If you’ve tried all these fixes and still struggle with dead zones, only then should you consider investing in a mesh Wi-Fi system or a more powerful router. But for most homes, these nine fixes should be more than enough to ensure strong, reliable Wi-Fi in every room.
FAQs
1. Why is my Wi-Fi strong in one room but weak in another?
Wi-Fi signals can weaken due to distance from the router, thick walls, metal objects, or electronic interference. Each of these factors can reduce signal strength in certain parts of your home.
2. Can I boost my Wi-Fi without buying a new router?
Yes! You can reposition your router, update its firmware, switch frequency bands, and use DIY solutions like foil reflectors or adjusting antennas to improve signal without buying new equipment.
3. Is 5GHz Wi-Fi better than 2.4GHz?
It depends on your needs:
- 5GHz offers faster speeds but shorter range
- 2.4GHz covers longer distances and penetrates walls better
For rooms near the router, 5GHz is ideal. For distant rooms, stick with 2.4GHz.
4. How do I find the best channel for my Wi-Fi?
Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app (like WiFi Analyzer or Airport Utility) to scan for the least crowded channel, then log in to your router’s admin panel to switch to that channel.
5. What are powerline adapters, and do they really work?
Powerline adapters use your home’s electrical wiring to transmit internet between rooms. They’re especially useful in hard-to-reach areas where Wi-Fi is weak and can deliver high-speed performance.
6. What’s the best position for my router?
Place your router:
- Centrally in your home
- 4–6 feet off the ground
- Away from walls, appliances, and electronics
Avoid hiding it behind furniture or inside cabinets.
7. How do I update my router’s firmware?
Log in to your router’s admin panel using its IP address (found on the router). Navigate to Firmware Update, then check for and install available updates. Many modern routers also support auto-updates via mobile apps.
8. Can mirrors or metal furniture affect Wi-Fi?
Yes. Mirrors, metal shelves, and appliances can reflect or absorb Wi-Fi signals, causing signal disruption. Try relocating your router or furniture to improve signal path.
9. What is QoS, and how does it help with weak signals?
Quality of Service (QoS) lets you prioritize internet traffic—like video calls or streaming—so they get more bandwidth, reducing lag or buffering even on weaker connections.
10. How do I know which fix is actually working?
Use tools like Speedtest.net or Fast.com before and after applying changes. You can also install a Wi-Fi analyzer app to see signal strength (measured in dBm)—closer to 0 is better.





